
I am currently a first-year PhD student at the National University of Singapore, supervised by Prof. Mengling Feng.
Reviewer for NIPS, IJCAI, ACM TIST, with over 10 papers reviewed.
Research Interests: Trustworthy and Agentic LLM • Multi-modality Intelligence in Healthcare
Looking for a summer 26' internship!! 🙏
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("zhihuichen.netlify.app").
Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
zhihuichen.netlify.app", so that your site can be accessed directly at "http://zhihuichen.netlify.app".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 National University of SingaporePh.D. in Artificial IntelligenceJan. 2025 - present
National University of SingaporePh.D. in Artificial IntelligenceJan. 2025 - present -
 The University of Hong KongM.Sc. in Artificial IntelligenceSep. 2022 - Jul. 2024
The University of Hong KongM.Sc. in Artificial IntelligenceSep. 2022 - Jul. 2024 -
 The Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenB.Sc. in Statistics, Data Science StreamSep. 2018 - May. 2022
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, ShenzhenB.Sc. in Statistics, Data Science StreamSep. 2018 - May. 2022
Experience
-
 StepFun AI Intelligent TechnologyLLM Research InternJan. 2025 - June. 2025
StepFun AI Intelligent TechnologyLLM Research InternJan. 2025 - June. 2025 -
 The Chinese University of Hong KongResearch StaffSep. 2024 - Jan. 2025
The Chinese University of Hong KongResearch StaffSep. 2024 - Jan. 2025
Honors & Awards
-
Full Ph.D. Scholarship, National University of Singapore2025
-
Outstanding College Graduate, CUHK-Shenzhen Harmonia College2022
-
Undergraduate Research Excellence Award, CUHK-Shenzhen2021
News
Selected Publications (view all )
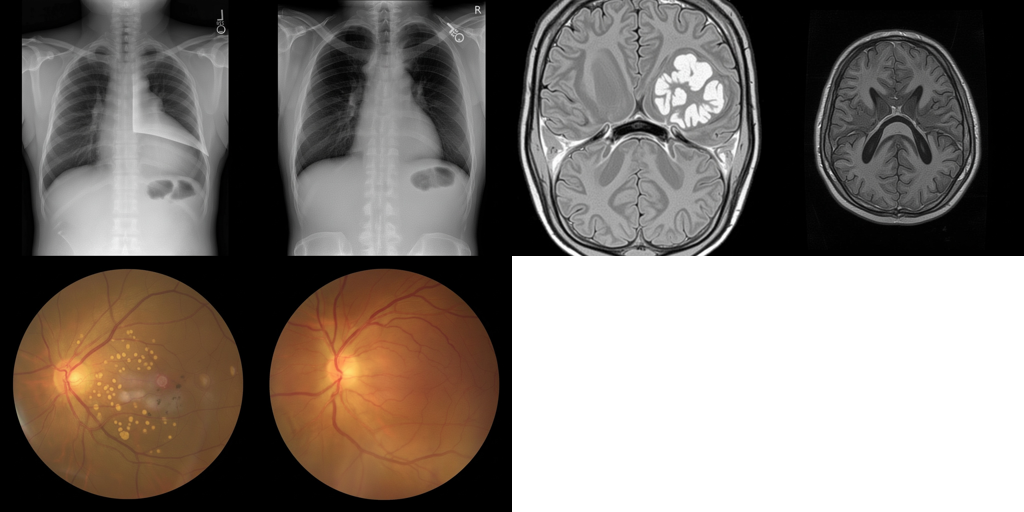
Med-Banana-50K: A Large-Scale Cross-Modality Dataset for Medical Image Editing 🔗
Zhihui Chen, et al.
arXiv preprint 2025
Recent advances in multimodal large language models have enabled remarkable medical image editing capabilities. However, the research community's progress remains constrained by the absence of large-scale, high-quality, and openly accessible datasets built specifically for medical image editing with strict anatomical and clinical constraints. We introduce Med-Banana-50K, a comprehensive 50K-image dataset for instruction-based medical image editing spanning three modalities (chest X-ray, brain MRI, fundus photography) and 23 disease types. Our dataset is constructed by leveraging Gemini-2.5-Flash-Image to generate bidirectional edits (lesion addition and removal) from real medical images. What distinguishes Med-Banana-50K from general-domain editing datasets is our systematic approach to medical quality control: we employ LLM-as-Judge with a medically grounded rubric and history-aware iterative refinement up to five rounds.
Med-Banana-50K: A Large-Scale Cross-Modality Dataset for Medical Image Editing 🔗
Zhihui Chen, et al.
arXiv preprint 2025
Recent advances in multimodal large language models have enabled remarkable medical image editing capabilities. However, the research community's progress remains constrained by the absence of large-scale, high-quality, and openly accessible datasets built specifically for medical image editing with strict anatomical and clinical constraints. We introduce Med-Banana-50K, a comprehensive 50K-image dataset for instruction-based medical image editing spanning three modalities (chest X-ray, brain MRI, fundus photography) and 23 disease types. Our dataset is constructed by leveraging Gemini-2.5-Flash-Image to generate bidirectional edits (lesion addition and removal) from real medical images. What distinguishes Med-Banana-50K from general-domain editing datasets is our systematic approach to medical quality control: we employ LLM-as-Judge with a medically grounded rubric and history-aware iterative refinement up to five rounds.
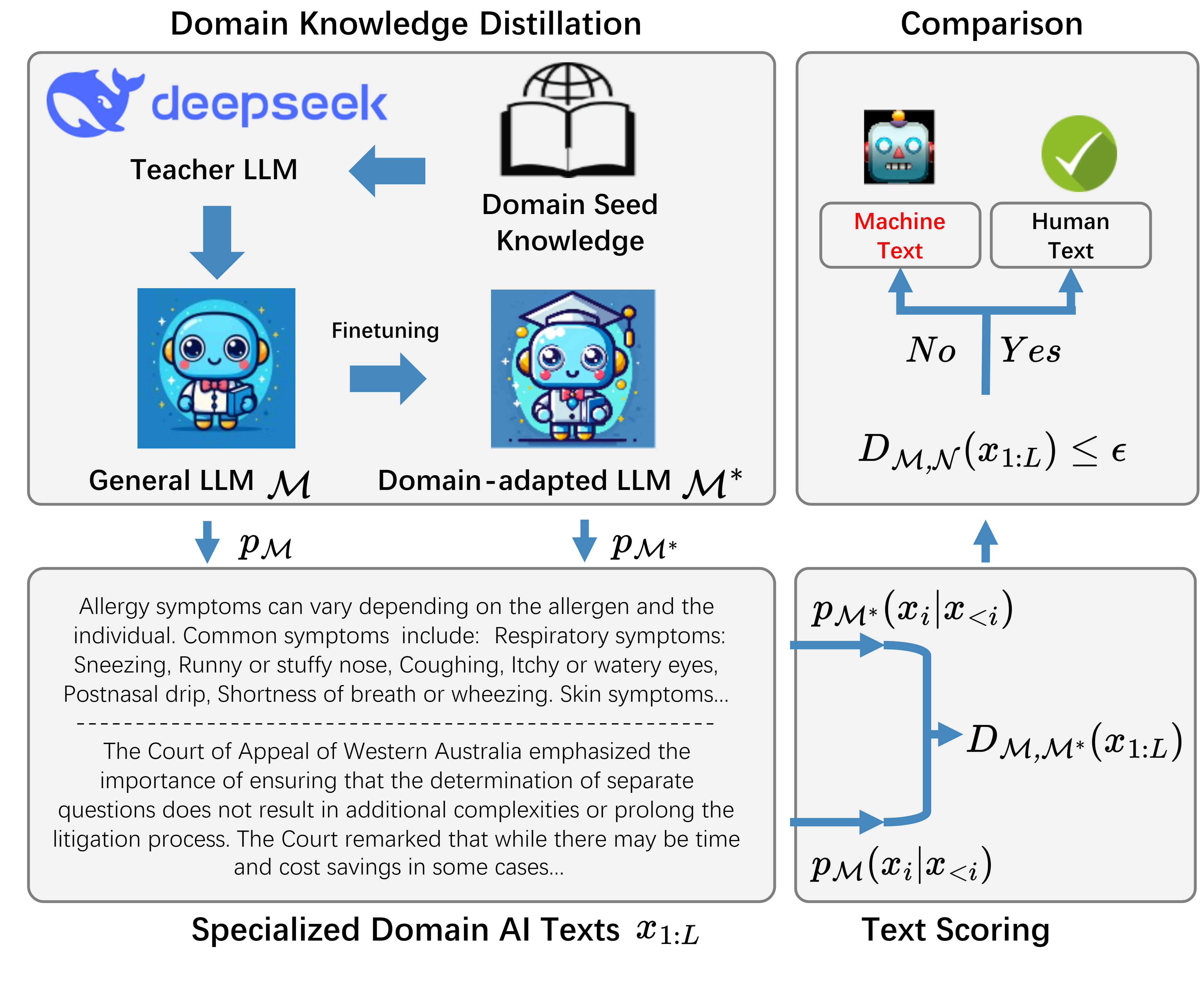
DivScore: Zero-Shot Detection of LLM-Generated Text in Specialized Domains 🔗
Zhihui Chen, Kai He, Yucheng Huang, Yunxiao Zhu, Mengling Feng
Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025 Main Conference" data-zh=" 主会议"> Main Conference
Detecting LLM-generated text in specialized and high-stakes domains like medicine and law is crucial for combating misinformation and ensuring authenticity. We propose DivScore, a zero-shot detection framework using normalized entropy-based scoring and domain knowledge distillation to robustly identify LLM-generated text in specialized domains. Experiments show that DivScore consistently outperforms state-of-the-art detectors, with 14.4% higher AUROC and 64.0% higher recall at 0.1% false positive rate threshold.
DivScore: Zero-Shot Detection of LLM-Generated Text in Specialized Domains 🔗
Zhihui Chen, Kai He, Yucheng Huang, Yunxiao Zhu, Mengling Feng
Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025 Main Conference" data-zh=" 主会议"> Main Conference
Detecting LLM-generated text in specialized and high-stakes domains like medicine and law is crucial for combating misinformation and ensuring authenticity. We propose DivScore, a zero-shot detection framework using normalized entropy-based scoring and domain knowledge distillation to robustly identify LLM-generated text in specialized domains. Experiments show that DivScore consistently outperforms state-of-the-art detectors, with 14.4% higher AUROC and 64.0% higher recall at 0.1% false positive rate threshold.